本文内容搬运自:
这篇survey上传于2020/3/28,对此之前的Crowd Counting进行了review,很全面。
Awesome家族的一员,包括Datasets、Papers、Leaderboard。
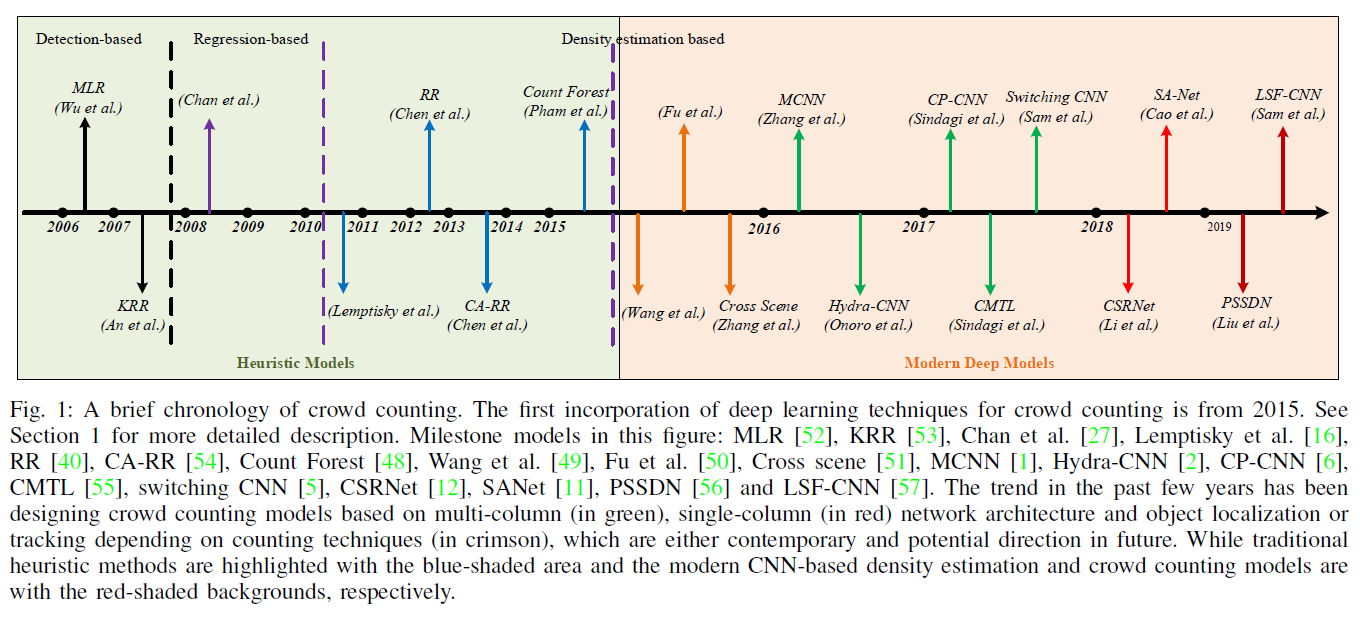
Milestone
Methods
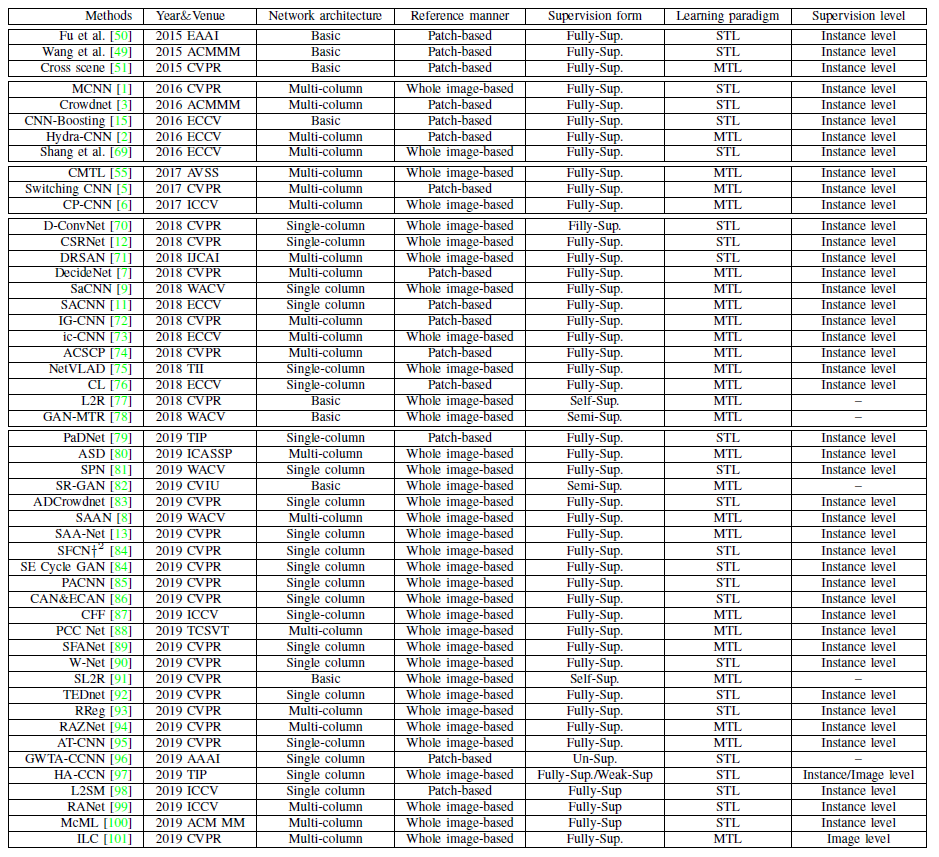
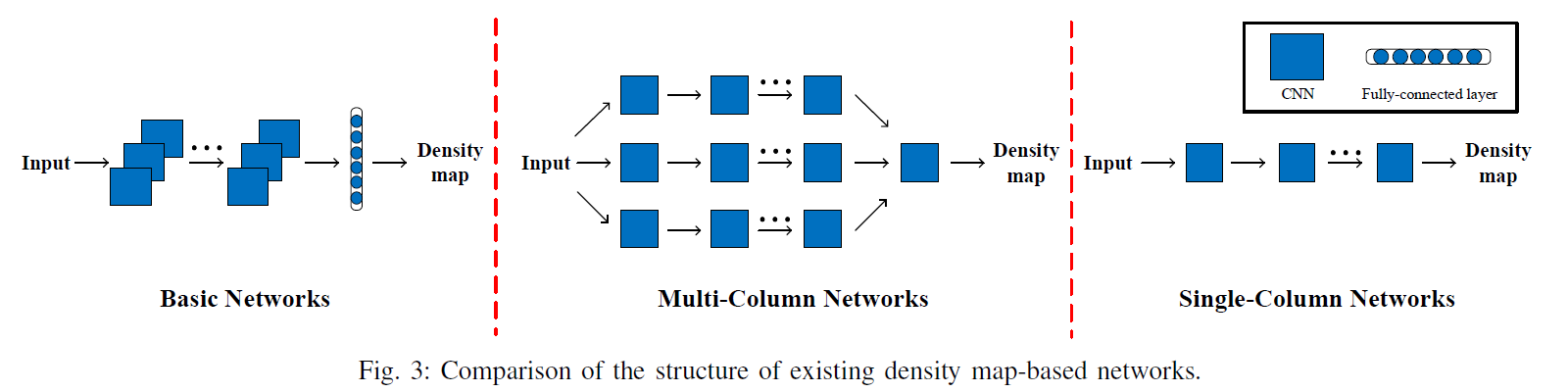
- Network architecture
- Inference manner
Patch-based methods: This inference manner is required to train using patches randomly cropped from the image. In the test phase, using a sliding window spreads over the whole test image, and getting the estimations of each window and then assembling them to obtain the final total count of the image.Whole image-based methods: Patch-based methods always neglect global information and burden much computation cost due to the sliding window operation. Thus the whole image-based methods usually take the whole image as input, and output corresponding density map or a total number of the crowds, which is more convergence but may lose local information sometimes.- Supervision form
Fully-supervised methods: The vast majority of CNN-based crowd counting methods rely on large-scale accurately hand-annotated and diversified data. However, the acquisition of these data is a time-consuming and more onerous labeling burden than usual. Beyond that, due to the rarely labeled data, the methods may suffer from the problem of over-fitting, which leads to a significant degradation in performance when transferring them in the wild or other domains. Therefore, training data with less or even without labeled annotations is a promising research topic in the future.Un/semi/weakly/self-supervised methods: Un/semisupervised learning denotes that learning without or with a few ground-truth labels, while self-supervised learning represents that adding an auxiliary task which is different from but related to supervised tasks. Some methods exploit unlabeled data for training have achieved comparative performance in contrast with supervised methods.- Learning paradigm
Single-task based methods: The classical methodology is to learn one task at one time, i.e., single-task learning. Most CNN-based crowd counting methods belong to this paradigm, which generally generates density maps and then sum all the pixels to obtain the total count number, or the count number directly.Multi-task based methods: More recently, inspired by the success of multi-task learning in various computer vision tasks, it has shown better performance by combing density estimation and other tasks such as classification, detection, segmentation, etc. Multi-task based methods are generally designed with multiple subnets; besides, in contrast to pure single column architecture, there may be other branches corresponding to different tasks. In summary, multi-task architectures can be regarded as the cross-fertilize between multi-column and single-column but different from either one.- Supervision level
Instance-level supervision: Most crowd density estimation methods are based on instance-level (point-level or bounding box) supervision, which needs hand-labeled annotations for each instance location.Image-level supervision: Image-level supervisionbased methods need to count the number of instances within or beyond the subitizing range, which do not require location information. It can be regarded as estimating the count at one shot or glance.
Performance
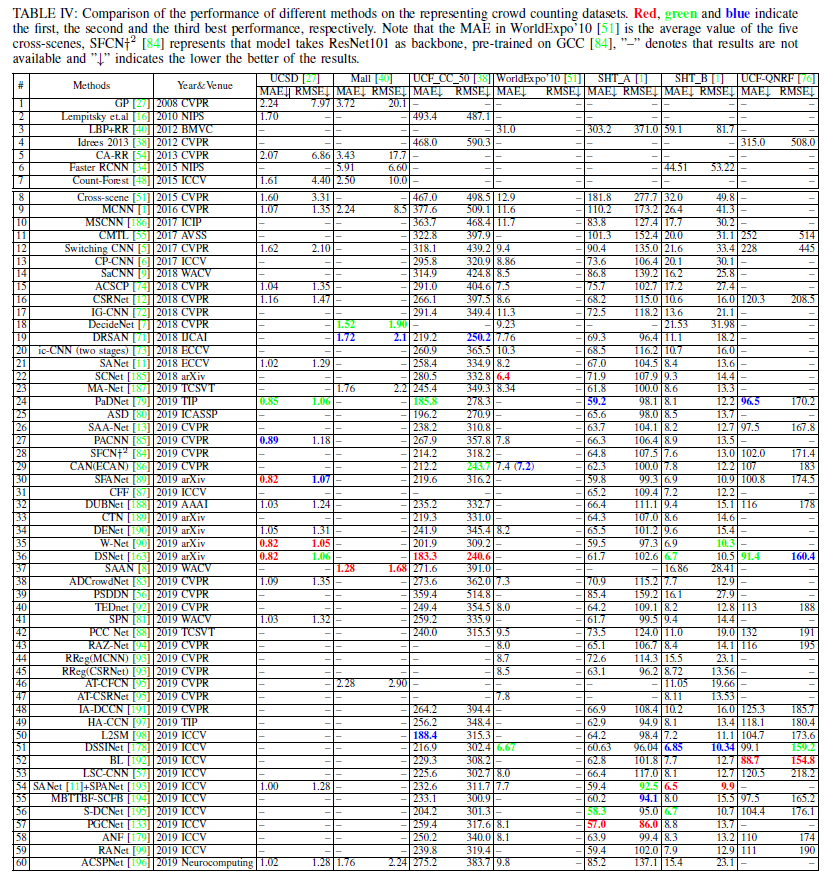
Properties of SOTA methods
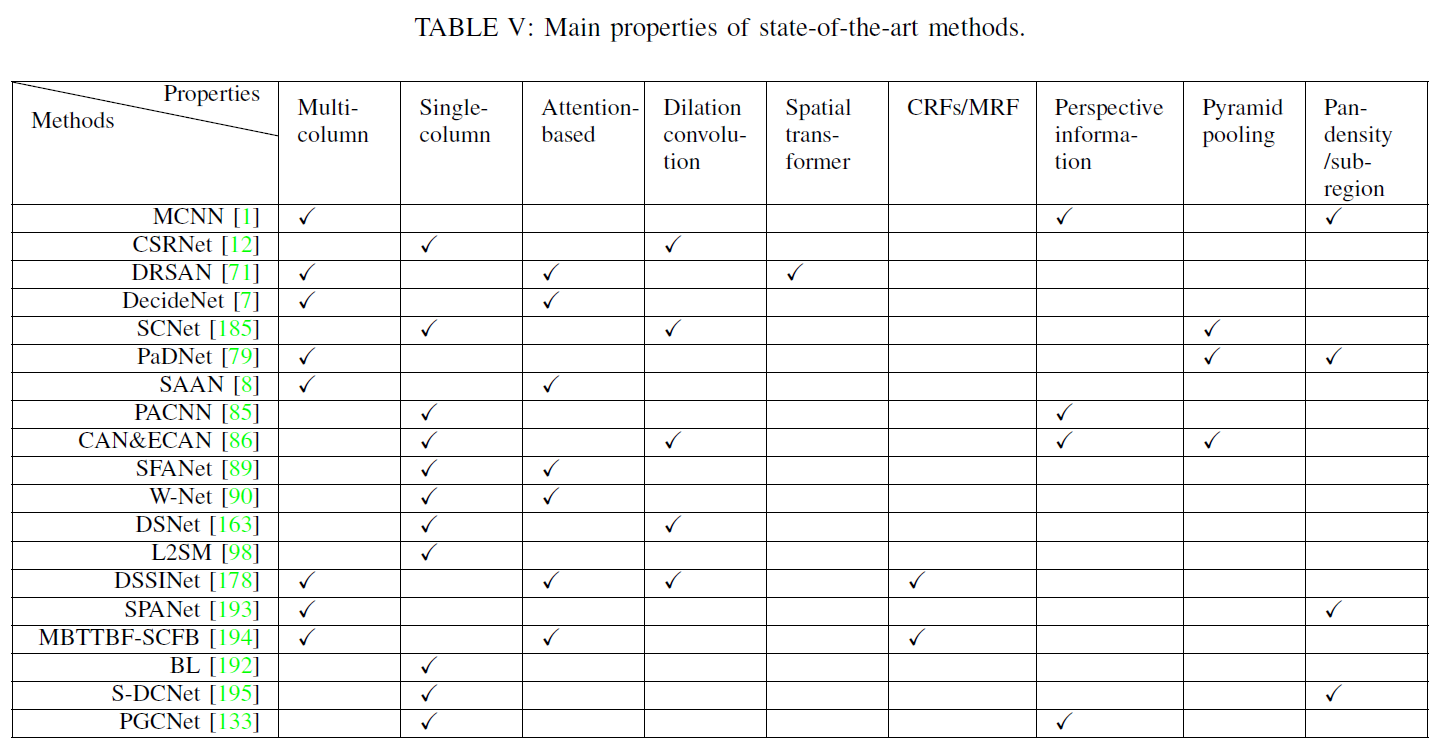
Dataset
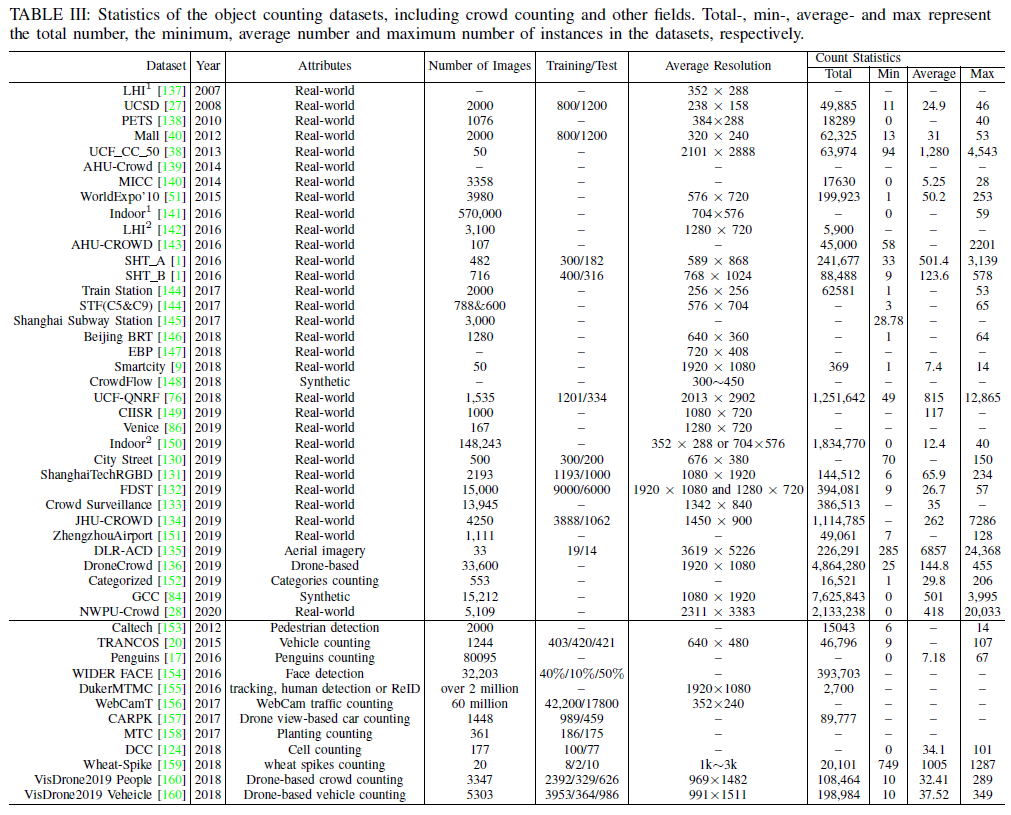
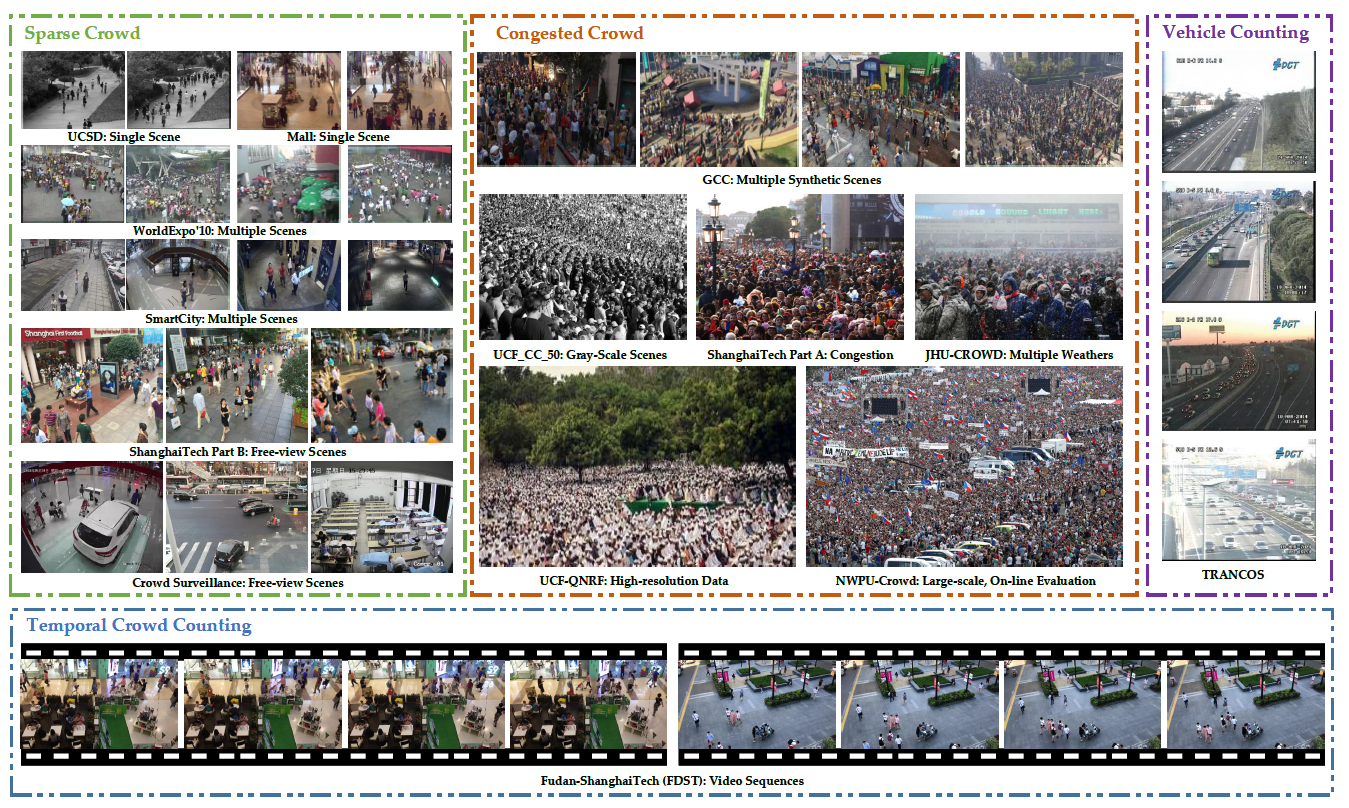
Evaluation metrics
-
Image-Level
- MAE ——
Mean Absolute Error
- RMSE ——
Mean Square Error
- GAME(L) ——
Grid Average Mean Absolute Error
- MPAE ——
mean pixel-level absolute error
- MAE ——
-
Pixel-Level
- PSNR ——
Peak Signal to Noise Ratio - SSIM ——
Structural Similarity Index Masure
- PSNR ——
-
Point-Level
- AP ——
Average Precision - AR ——
Average Recall
- AP ——
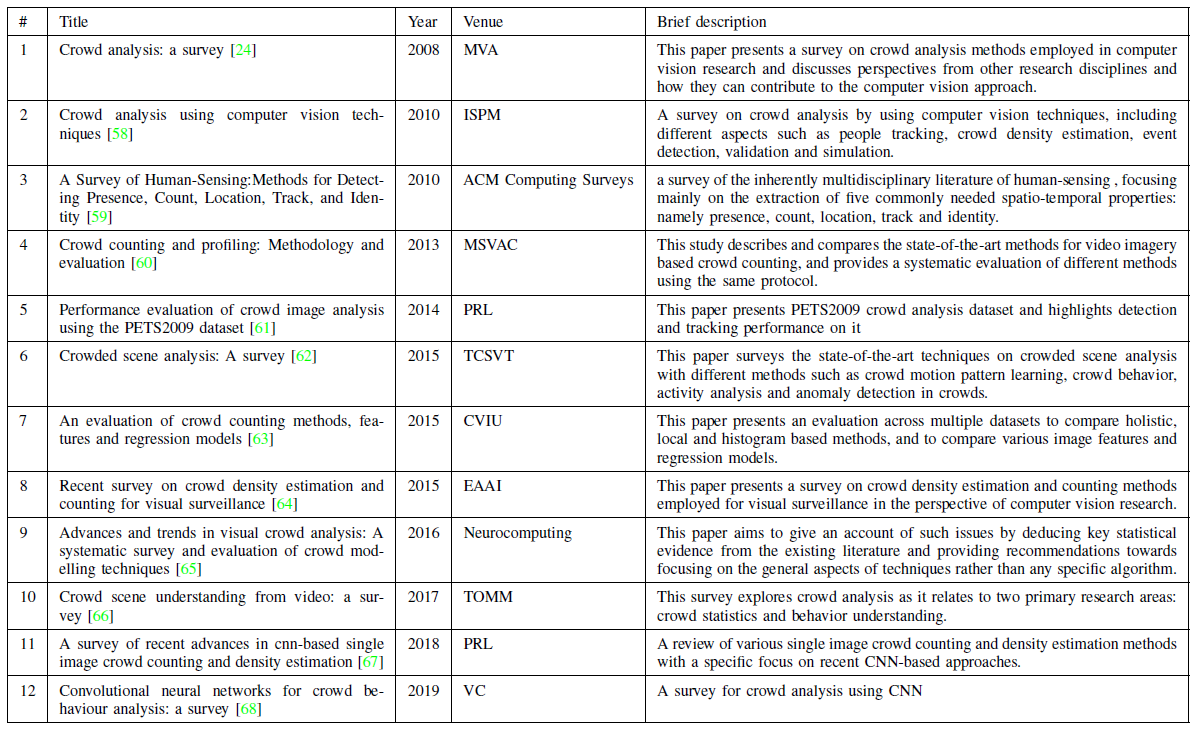
Other survey